Test assembly
Tests, or assessments, are assembled from individual Items. Items are built from Interactions, which are based on exercises such as multiple choice questions. Tests define the order of items, as well as how and when they are presented to the Test-taker. They also define the constraints and settings, including those related to time and navigation policies. Tests may be built from building blocks called Item Sections that logically sort Items into groups, making configuring a Test easier.
In TAO, assessments are assembled from individual items that are later delivered to test-takers through an automated Delivery system. If there are enough items within a test, they can be sorted and grouped into item sections according to any logical set of criteria. Tests should be given an appropriate title which helps test-takers to accurately identify the assessment if it appears in a list of other assessments which the test-taker must also take at the same time. Test designers must consider issues such as whether the test-taker will need to follow a linear path through a test – where questions need to be answered in a specific order, with no option to revisit them later – or whether questions can be answered in any order and revisited if desired. Time limitations and feedback are also important elements in successful test design.
This section provides an overview of how to put a new test together. See Creating a test for information on how to do this. (To create a new test, items first need to be created, so that they can be used in assessments. See Creating a test item for further information.)
The sub-section Configuring tests describes the choices you will need to make along the way: you will need to assign certain properties to your test – and there are four levels on which to do this, from the top test level down to the individual item level.
The image below shows a sample test, the SDG Quiz (on the Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations).
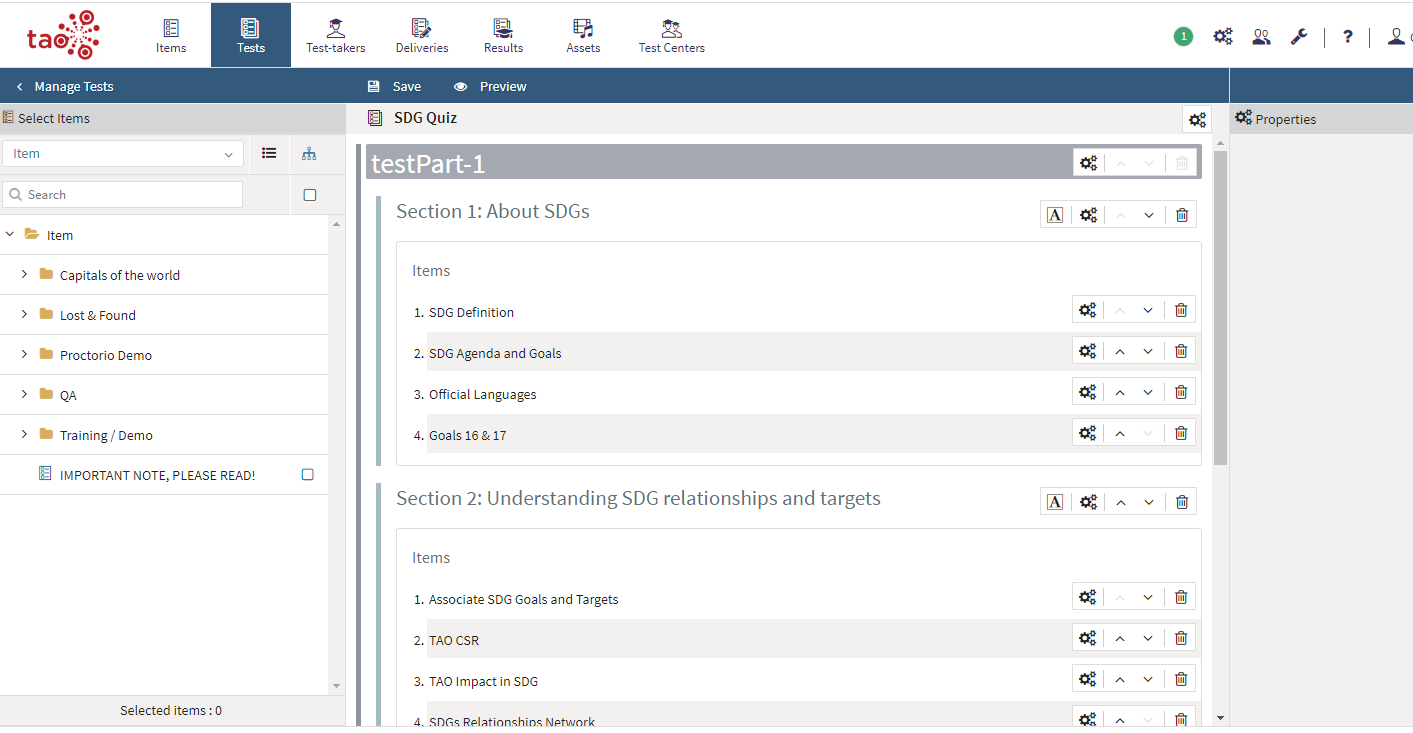
Sample test
Possible ways of scoring your test are described in Scoring tests, and Previewing a test shows how to check that your test functions correctly.
Finally, there is a chapter on how to publish a test – i.e. convert it into a deliverable form.
